goroutine栈的申请与释放
admin
- 3 minutes read - 454 words对于提高对 stack 的使用效率,避免重复从heap中分配与释放,对其使用了 pool 的概念,runtime 里为共提供了两个pool, 分别为 stackpool ,另一个为 stackLarge。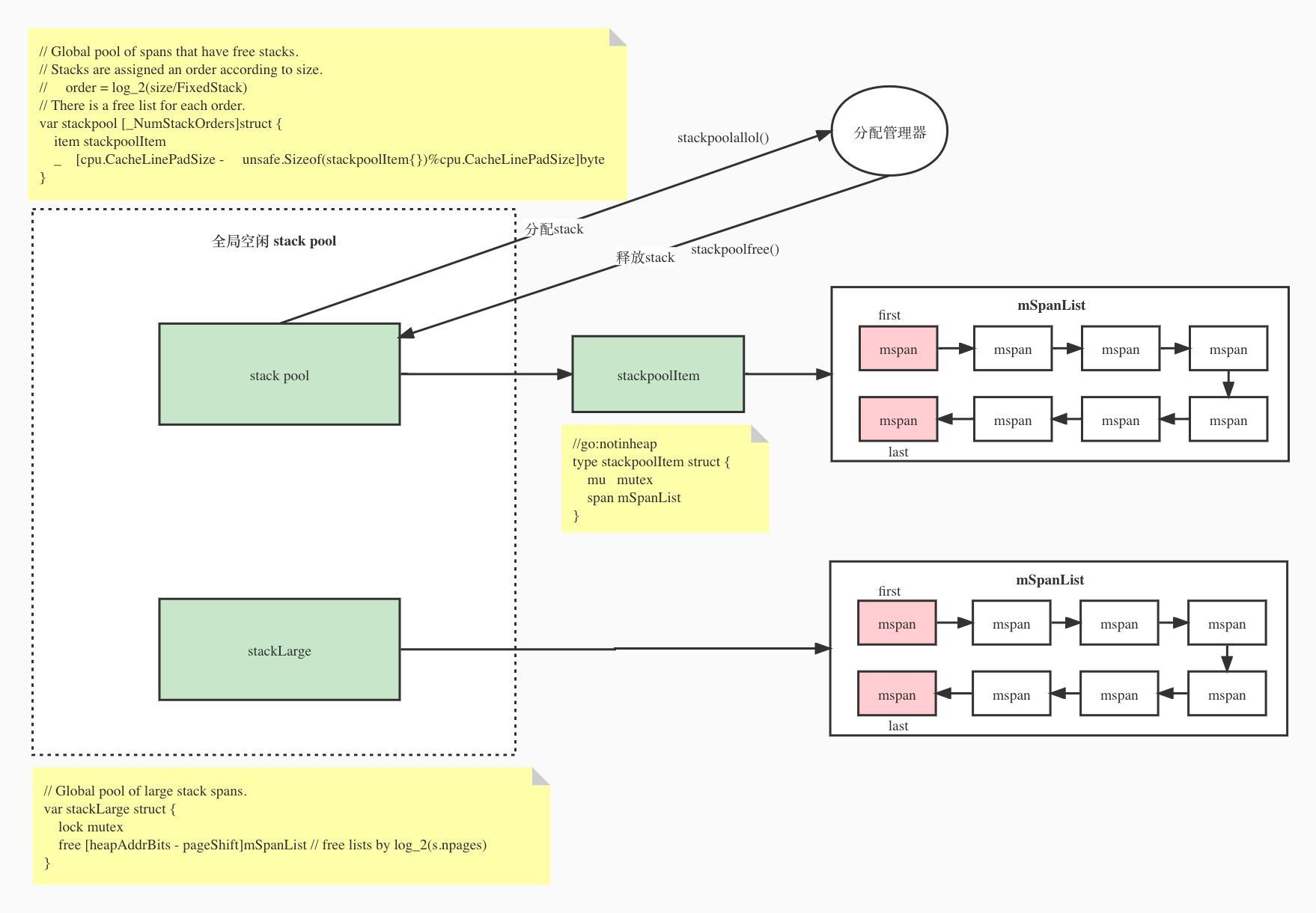 stack pool
stack pool
stackpool: 16b~32k 对应通用的大小的stack。获取时通过调用 stackpoolalloc(), 释放时调用 stackpoolfree()。
stackLarge:对应 > 32K 的 stack
在程序全局调度器 初始化 时会通过调用 stackinit() 实现对 stack 初始化。
当我们执行一个 go func() 语句的时候,runtime 会通过调用 newproc() 函数来创建G。而内部真正创建G的函数为 [newproc1()](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/proc.go#L3990-L4098),在没有G可以复用的情况下,会通过 newg = malg(_StackMin) 语句创建一个包含stack的G。
// Allocate a new g, with a stack big enough for stacksize bytes.
func malg(stacksize int32) *g {
newg := new(g)
if stacksize >= 0 {
stacksize = round2(_StackSystem + stacksize)
systemstack(func() {
newg.stack = stackalloc(uint32(stacksize))
})
newg.stackguard0 = newg.stack.lo + _StackGuard
newg.stackguard1 = ^uintptr(0)
// Clear the bottom word of the stack. We record g
// there on gsignal stack during VDSO on ARM and ARM64.
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(newg.stack.lo)) = 0
}
return newg
}
对于新创建的g,需要通过调用 [stackalloc()](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/stack.go#L321-L419) 函数为其分配 stacksize 大小stack,那么分配操作它又是如何工作的呢?
stack的申请
根据申请stack的大小分两种情况,一种是 small stack,另一种是 large stack,两者采用不同的申请策略。主要涉及了内存申请策略,如果对golang 的内存管理比较了解的话,这块理解起来就很容易了。建议先阅读一下这篇文章《 Golang 内存组件之mspan、mcache、mcentral 和 mheap 数据结构》。
func stackalloc(n uint32) stack {
...
var v unsafe.Pointer
if n < _FixedStack<<_NumStackOrders && n < _StackCacheSize {
order := uint8(0)
n2 := n
for n2 > _FixedStack {
order++
n2 >>= 1
}
var x gclinkptr
if stackNoCache != 0 || thisg.m.p == 0 || thisg.m.preemptoff != "" {
// thisg.m.p == 0 can happen in the guts of exitsyscall
// or procresize. Just get a stack from the global pool.
// Also don't touch stackcache during gc
// as it's flushed concurrently.
lock(&stackpool[order].item.mu)
x = stackpoolalloc(order)
unlock(&stackpool[order].item.mu)
} else {
c := thisg.m.p.ptr().mcache
x = c.stackcache[order].list
if x.ptr() == nil {
stackcacherefill(c, order)
x = c.stackcache[order].list
}
c.stackcache[order].list = x.ptr().next
c.stackcache[order].size -= uintptr(n)
}
v = unsafe.Pointer(x)
} else {
...
}
return stack{uintptr(v), uintptr(v) + uintptr(n)}
}
对于 small stack 以可以分两种情况:
- 有
P:会直接通过从当前 G 绑定的P中的mcache字段申请,这个字段可以理解为内存资源中心,里面包含有多种不同规格大小的内存块,根据申请大小找到一个可以满足其大小的最小规格的内存区域。 - 无
P:调用[stackpoolalloc](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/stack.go#L182-L220) [(](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/stack.go#L182-L220) [)](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/stack.go#L182-L220)会直接从全局stack pool中获取
用户需要重点关注下 stackcacherefill() 函数。
func stackalloc(n uint32) stack {
...
var v unsafe.Pointer
if n < _FixedStack<<_NumStackOrders && n < _StackCacheSize {
...
} else {
var s *mspan
npage := uintptr(n) >> _PageShift
log2npage := stacklog2(npage)
// Try to get a stack from the large stack cache.
lock(&stackLarge.lock)
if !stackLarge.free[log2npage].isEmpty() {
s = stackLarge.free[log2npage].first
stackLarge.free[log2npage].remove(s)
}
unlock(&stackLarge.lock)
lockWithRankMayAcquire(&mheap_.lock, lockRankMheap)
if s == nil {
// Allocate a new stack from the heap.
s = mheap_.allocManual(npage, spanAllocStack)
if s == nil {
throw("out of memory")
}
osStackAlloc(s)
s.elemsize = uintptr(n)
}
v = unsafe.Pointer(s.base())
}
...
return stack{uintptr(v), uintptr(v) + uintptr(n)}
}
对于 large stack 而言,先从 [stackLarge](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/stack.go#L152-L156) 全局对象 large stack spans 池中查找。
如果未找到的话,则调用 osStackAlloc() 和 [mheap_.allocManual()](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/mheap.go#L922-L944) 函数直接从 heap 中直接申请并注册这块内存。
最后根据找到内存的起始地址(低地址)和 申请大小n,返回 stack 结构体。
总结
从上面可以看到对 stack 的存放有两个地方,一个是全局 stack pool ,另一个就是 P 中的 mcache 字段。分配 stack 时需要考虑当前 g 的运行模式,如果运行在 systemstack 则需要直接从 stack pool中分配stack,否则直接从 p.mcache 分配即可。
stack的释放
对于stack的释放,实现函数为 [stackfree()](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/stack.go#L421-L496)。
在资源申请时根据其申请大小分为两种情况,同样对于stack的释放也是一样。对于small stack 来讲,从哪里申请的用完再放回去即可,操作对象仍是 P下面的 mcache 字段。
而对于 large stack 来讲,则需要放回 [stackLarge](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/stack.go#L152-L156) 全局变量以便复用,避免重复申请产生的开销;但如果当前GC正处于清扫阶段,则直接调用 osStackFree() 和 [mheap_.freeManual()](https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16.3/src/runtime/mheap.go#L1422-L1438) 来释放内存。
对于g中stack的释放触发条件有:
- 当一个g运行结束的时候,可能会释放stack(只是有可能)参考: https://blog.haohtml.com/archives/23437;
- GC期间会清理所有包含stack的g,直接释放完所有g的stack, 然后再将这些g放在不包含stack的
sched.gFree.noStack列表中(这里指的是全局调度器 sched ),参考: https://blog.haohtml.com/archives/27003; - 其它